LiFePO4 battery continues to dominate the battery storage arena in 2023 thanks to their high energy density, compact size, and long cycle life.
If you’re looking to prolong your battery life while still maintaining its performance, then knowing the best ways to charge a LiFePO4battery will really come in handy.
There are several lithium battery chemistries currently on the market, but the LiFePO4 is undoubtedly the best one to date, particularly for applications that require a large battery bank.
Due to its extremely stable chemistry, LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries provide a much safer option than other lithium technologies, which can lead to a fire if mishandled.
The LiFePO4 batteries are also much more resistant and can withstand electrical and thermal abusive conditions. This means they can stand the test of time, performing a large number of cycles without compromising their performance.
Despite being more expensive than its lithium or lead-acid counterparts, LiFePO4 batteries are an excellent long-term investment if — and that’s a critical condition — they are properly maintained.
What applications use LiFePO4 batteries?
Thanks to their high power specs (W/kg), energy density (Wh/kg), and extended life duration (up to 10 years), LiFePo4 batteries have many applications. They are safe enough to be used for both stationary and mobile applications.
Below, I have listed some of the many applications of LiFePO4 batteries:
-
- Energy Storage systems (ESS).
- Solar batteries, along with solar panels.
- Portable solar generators for camping and DIY systems.
- EV batteries An application that requires high power, storage capacity, and durability. LiFePo4 batteries can provide strong pulses of current during car acceleration.
- Solar water pumping systems.
- Electric bikes and scooters.
This article will provide the 4 ways to charge a LiFePO4 battery. This will assist those of you who’re aiming to get the most out of your battery system and make it a worthwhile investment.
Do LiFePO4 Batteries Need A Special Charger?
This is a very common question that comes up when one considers switching to Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries.
The short answer is no — a special charger is not exactly a requirement. What is required, though, is that the charger supplies the battery with the appropriate charging specifications.
But what does that mean? What are the charging specifications of a LiFePO4 battery?
To answer these questions, let’s first revisit a few relevant concepts:
Charging
Charging a battery simply means applying an external voltage to force the flow of electrons (current) from the cathode to the anode. While discharging, the electrons flow in the opposite direction.
Voltage
Voltage is a force that makes electric charges move. In other words, voltage is the pressure in which the current moves through an electrical system.
Batteries are an assembly of several cells. The number of cells in a battery will determine its nominal voltage.
Lithium Iron Phosphate cells have a nominal voltage of 3.2V, so placing four cells in series provides a nominal voltage of 12.8V. Lead-acid batteries cells have a 2V output, so six cells in series result in a 12V nominal voltage.
This nominal voltage compatibility makes the LiFePO4 a viable alternative to lead-acid batteries.
For the current to flow to the battery – and effectively charge it – the external voltage applied should be slightly higher than the open-circuit battery voltage.
But if the applied voltage is too high or too low, the battery won’t charge because the BMS protection will kick in. Or, in a worst-case scenario, the battery will die.
So, to properly charge a LiFePO4 battery, make sure to respect the voltage specifications provided by the battery manufacturer.
Below is a table showing the usually recommended charging parameters of a LiFePO4 battery:
| System Voltage | Charging Parameters |
|---|---|
| 12V | 14V – 14.6V |
| 24V | 28V – 28.6V |
| 36V | 42V – 42.8V |
| 48V | 56V – 57.8V |
This table shows that you can charge your 12V LiFePO4 battery with any type of charging equipment, as long as the charging voltage is within the 14V to 14.6V range.
But of course, just because you can, doesn’t mean you should. So here we present the 4 ways to charge your LiFePO4.
4 Ways To Charge A LiFePO4 Battery
1. Using A Smart Charger
Ok, we know this might sound obvious, but it’s simply the truth — we couldn’t just skip this one.
One of the best ways to charge a battery is using a charger that matches the battery’s chemistry since each one has its particularities.

A smart charger can be adjusted according to the LiFePO4 battery charging profile. This maximizes the battery’s performance and lifespan by using an optimized charging technology.
LiFePO4 Battery Charging Profile:
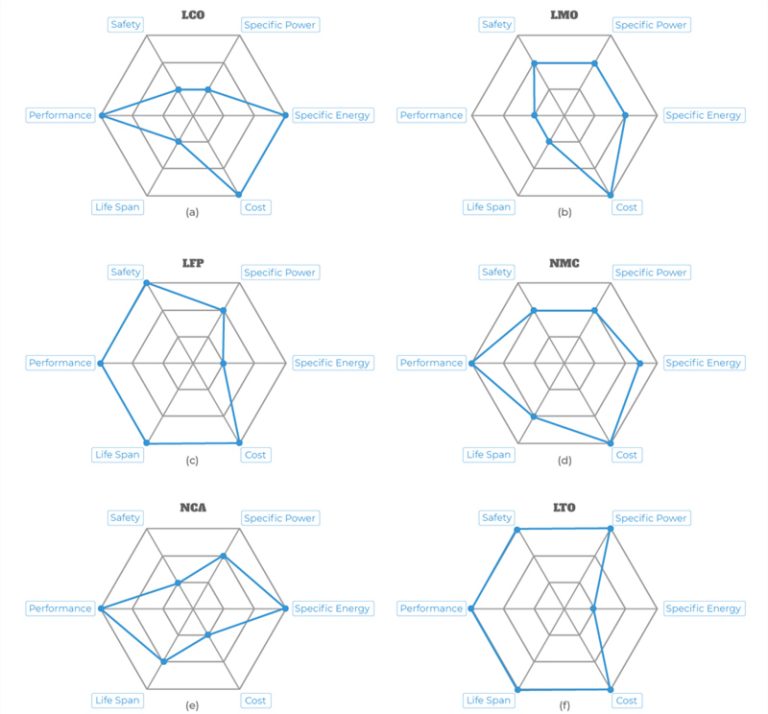
Having looked at the graph, you’ll see that there are two stages:
Stage 1, “bulk” — The battery is provided with a constant charging current, while the voltage gradually increases. This stage usually takes 1 to 2 hours.
Stage 2, “absorption” — When the charging voltage reaches a little over 14V, the state of charge of the LiFePO4 battery is at around 90%. At this point, to reach full charge, the charging voltage becomes constant, while the charging current decreases to around 5% to 10% of the battery’s Ah rating.
Unlike Lead-acid technologies, it’s not necessary to float charge LiFePO4 batteries. In fact, they can last longer if not constantly kept at 100%.
In addition, LiFePO4 batteries don’t need equalization, nor do they require temperature compensation (required when charging a lead-acid battery). So a proper LiFePO4 charger should not perform these features.
To summarize, you can program a smart charger to provide the LiFePO4 with its specific charging conditions. This way, you can’t go wrong.
2. Using A Lead-Acid Battery Charger
So you’re considering switching your lead-acid deep cycle batteries to brand new LiFePO4 batteries (smart move) and you’re wondering if you’ll need a new charger?
The good news — not necessarily! Most lead-acid battery chargers will do the job just fine.
As long as the charging settings are within the acceptable parameters for LiFePO4 batteries, it’s possible to charge these batteries with lead-acid battery chargers.
Because lead-acid batteries (AGM and Gel) and LiFePO4 have similar nominal voltages, AGM and Gel charging algorithms typically meet the LiFePO4 charging voltage requirements.
An important difference between these batteries is that, unlike the lead-acid batteries, LiFePO4 batteries don’t rapidly lose charge when disconnected. This means that float charging is not necessary.
So when using a lead-acid battery charger to charge a LiFePO4 battery, the float charge option should be switched off. If that’s not possible, the float stage voltage should be set low enough so it can never be reached. Setting the floating voltage under 13.6V is good enough.
In addition, LiFePO4 batteries don’t need equalization or temperature compensation. So disabling these features is also necessary.
If these required adjustments cannot be made to the lead-acid battery charger, then buying an appropriate LiFePO4 battery charger (or a smart charger) is highly recommended.
3. Using Solar Panels
Using a solar energy system to charge LiFePO4 batteries is not only possible but highly encouraged.
That’s because the energy being stored is not just being taken from another energy source (like shore power), it’s actually being generated by solar panels.
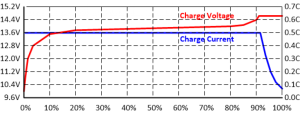
Whether in a home, a boat, or an RV, a solar energy system looks pretty much the same (as shown in the scheme above):
1. Solar panels: convert energy from the sunlight into electrical energy.
2. Charge controller: regulates the power output of the solar panels according to the battery’s charging requirements, avoiding battery overcharge.
3. Battery: stores the energy provided by the solar panels as chemical energy.
4. Inverter: converts direct current (produced by solar panels) into alternating current (which the appliances can actually use).
Once again, correctly sizing the components is key to maintaining the system running appropriately.
So using a charge controller that can efficiently charge the LiFePO4 battery – respecting its charging requirements – is crucial to ensure that the battery functions well and for a long time.
4. Using An Alternator (And A DC-DC Charger)
And last but not least, another great way to charge a LiFePO4 battery is using an alternator. This is a great solution for RVs and boats that have a battery storage setup.
What Is An Alternator?
An alternator is simply a generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It generates alternating current (hence the name), which the rectifier attached to the alternator then converts into direct current.
This device is an essential part of every combustion engine vehicle’s electrical system. It charges the starter battery, used to start the vehicle’s engine.
With a few adjustments, you can use this electrical system to charge your battery bank (in this case, LiFePO4 batteries) while driving your vehicle.
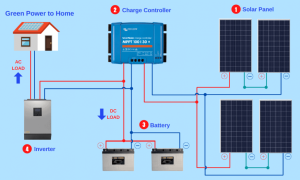
The above image shows a DC/DC charger as a necessary part of the system.
Because LiFePO4 batteries have a low internal resistance when not fully charged, they can draw any amount of current from the alternator, which can overheat the alternator and damage the battery.
A DC/DC charger acts by limiting the current drawn from the alternator, avoiding the overheating issue. It also regulates the output voltage to the required charging voltage of the LiFePO4 battery, protecting it from overcharging.
What Happens Inside A LiFePO4 Battery When It Is Charged?
Before we can successfully answer this question, here are a few important things to know:
Lithium Iron Phosphate cells are made of four main components:
- Cathode: LiFePO4
- Anode: Graphite (which stores lithium by intercalation)
- Electrolyte: Lithium Salts in organic solvent
- Separator: Polyethylene microporous membrane
Below is an illustration that helps to understand the charging process:
So when a LiFePO4 is charged, the application of external power forces the electrons to flow to the negative electrode. This result is the flow of lithium ions from the cathode to the anode.
When discharging, the opposite happens. Lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode, while electrons flow to the positive electrode, through the load.
Once fully charged, the lithium ions in the battery are located mostly in the graphite, so there aren’t many electrons left to move from the cathode to the anode.
At this point, the application of external power should stop. Battery Management Systems detect when the battery is fully charged and cease the charging process, avoiding overcharging.
What Is The Safest Way To Charge A LiFePO4 Battery?
Unlike other lithium battery chemistries, the LiFePO4 is very safe due to its superior thermal and chemical stability.
That’s because LiFePO4 is naturally a stable compound. The P – O bond (in the PO43- species) is quite strong, so when the battery is abused (overcharged or short-circuited), the oxygen atoms aren’t released so easily.
As a result, lithium iron phosphate cells are much harder to ignite. This is an important feature that makes them far superior to other Lithium battery chemistries.
Even though LiFePO4 batteries are a relatively safe technology, it’s extremely important to respect the charging parameters discussed in this article in order to avoid safety risks.
The safest way to charge these batteries would be respecting the exact specifications of the battery, in terms of voltage, optimal charging temperature, use of appropriate wires, etc, whether you use a LiFePO4 charger, a solar system, or any other way.
Tip: Always check your battery’s manual to see what the manufacturer recommends in terms of charging.
Final Thoughts
LiFePO4 batteries offer a great battery storage solution and can be used for various applications. Their thermal and chemical stability makes them very safe when compared to other battery chemistries, but this comes at a very high price – literally.
What makes this investment worthwhile is the promise of a very long battery life, with little maintenance and high performance. Manufacturers claim these batteries can perform thousands of cycles and last from 8 to 10 years if the recommended charging instructions are meticulously followed.
So now that you know the best ways to charge LiFePO4 batteries, which method will you use to charge yours?
LifePO4 Batteries Related Products:
Related Products Application:
LifePO4 Batteries Related Posts:
Tags: Lithium battery. LiFePO4 battery.